The basic principle of Interferential Therapy (IFT) is to utilize the significant physiological effects of low frequency (<250pps) electrical stimulation of nerves without the associated painful and somewhat unpleasant side effects sometimes associated with low frequency stimulation. Recently, numerous ‘portable’ interferential devices have become easily available. Despite their size, they are perfectly capable of delivering ‘proper’ interferential therapy, though some have limited functionality and ability for the practitioner to ‘set’ all parameters.
Interferential Current stimulation is very useful in the treatment of circulatory and muscular disorders, stiffness of joints, edema, and inflammation. If you suffer from health problems such as cumulative trauma disorders, body pain, joint injuries, or are pre or post orthopedic surgery, interferential current therapy is and important option.
Interferential current therapy has been in use for many years, and there have been numerous case studies and research reports that have documented its current therapy have fewer post-op complications compared to people who rely exclusively on medications for pain relief. It also helps in blood circulation and hastens the healing process by stimulating endorphins.
PRINCIPLES
To produce low frequency effects at sufficient intensity and at sufficient depth, patients can experience considerable discomfort in the superficial tissues (i.e. the skin). This is due to the impedance of the skin being inversely proportional to the frequency of the stimulation. [The barrier presented by the skin to the passage of an electric current is more complex than just impedance, or resistance, but will be regarded as such for the purpose of this explanation] In other words, the lower the stimulation frequency, the greater the impedance to the passage of the current & so, more discomfort is experienced as the current is ‘pushed’ into the tissues against this barrier. The skin impedance at 50Hz is approximately 3200 whilst at 4000Hz it is reduced to approximately 40. The result of applying a higher frequency is that it will pass more easily through the skin, requiring less electrical energy input to reach the deeper tissues & giving rise to less discomfort.
The effects of tissue stimulation with these ‘medium frequency’ currents (medium frequency in electromedical terms is usually considered to be 1KHz-100KHz) has yet to be established. It is unlikely to do nothing at all, but in terms of current practice, little is known of its physiological effects. It is not capable of direct stimulation of nerve in the common context of such stimulation, though some researchers are currently investigating this area.
Interferential therapy utilizes two of these medium frequency currents, passed through the tissues simultaneously, where they are set up so that their paths cross & they literally interfere with each other – hence another term that has been used in the past but appears to be out of favour at the moment – Interference Current Therapy. This interaction gives rise to an interference current (or beat frequency) which has the characteristics of low frequency stimulation – in effect the interference mimics a low frequency stimulation.
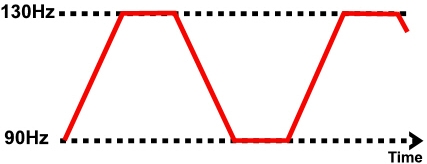
The exact frequency of the resultant beat frequency can be controlled by the input frequencies. If for example, one current was at 4000Hz and its companion current at 3900Hz, the resultant beat frequency would be at 100Hz, carried on a medium frequency 3950Hz amplitude modulated current.
By careful manipulation of the input currents it is possible to achieve any beat frequency that you might wish to use clinically. Modern machines usually offer frequencies of 1-150Hz, though some offer a choice of up to 250Hz or more. To a greater extent, the therapist does not have to concern themselves with the input frequencies, but simply with the appropriate beat frequency which is selected directly from the machine.
The magnitude of the low frequency interference current is (in theory) approximately equivalent to the sum of the input amplitudes. It is difficult to show categorically that this is the case in the tissues but it is reasonable to suggest that the resultant current will be stronger than either of the 2 input currents.
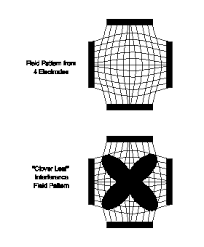
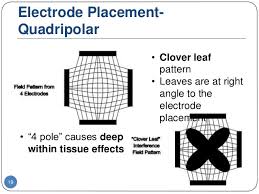
The use of 2 pole IFT stimulation is made possible by electronic manipulation of the currents – the interference occurs within the machine instead of in the tissues. There is no known physiological difference between the effects of IFT produced with 2 or 4 electrode systems. The key difference is that with a 4 pole application the interference is generated in the tissues and with a 2 pole treatment, the current is ‘pre modulated’ i.e. the interference is generated within the machine unit .
Whichever way it is generated, the treatment effect is generated from low frequency stimulation, primarily involving the peripheral nerves. There may indeed be significant effect on tissue other than nerves, but they have not as yet been unequivocally demonstrated. Low frequency nerve stimulation is physiologically effective (as with TENS and NMES) and this is the key to IFT intervention.
Physiological Effects
- Excitable tissues can be stimulated by low frequency alternating currents.
- Although to some extent, all tissues in this category will be affected by a broad range of stimulations.
- it is thought (Savage 1984) that different tissues will have an optimal stimulation band, which
- can be estimated by the conduction velocity of the tissue, its latency and refractory period.
- Sympathetic Nerve 1-5Hz
- Parasympathetic Nerve 10-150Hz
- Motor Nerve 10-50Hz
- Sensory Nerve 90-100Hz
- Nociceptive fibres 90-150Hz (?130Hz specific)
- Smooth Muscle 0-10Hz
The clinical application of I/F therapy can be based logically on this data together with a knowledge of physiological behavior of stimulated tissue. Selection of a wide treatment band can be considered less efficient than a smaller selective band in that by treating with a frequency range of say 1-100Hz, the appropriate treatment frequencies can be covered, but only for a relatively small percentage of the total treatment time. Additionally, some parts of the range might be counterproductive for the primary aims of the treatment.
- Pain relief
- Muscle stimulation
- Increased blood flow
- Reduction of edema
- In addition, claims are made for its role in stimulating healing and repair.
As I/F acts primarily on the excitable tissues, the strongest effects are likely to be those which are a direct result of such stimulation (i.e. pain relief and muscle stimulation). The other effects are more likely to be secondary consequences of these.
USES
1. Pain Relief:
Electrical stimulation for pain relief has widespread clinical use, thought the direct research evidence for the use of I/F in this role is limited. Logically one could use the higher frequencies (90-150Hz) to stimulate the pain gate mechanisms & thereby mask the pain symptoms. Alternatively, stimulation with lower frequencies (1-5Hz) can be used to activate the opoid mechanisms, again providing a degree of relief. These two different modes of action can be explained physiologically & will have different latent periods & varying duration of effect. It remains possible that relief of pain may be achieved by stimulation of the reticular formation at frequencies of 10-25Hz or by blocking C fibre transmission at >50Hz.
2. Muscle Stimulation:
Stimulation of the motor nerves can be achieved with a wide range of frequencies. Clearly, stimulation at low frequency (e.g. 1Hz) will result in a series of twitches, whist stimulation at 50Hz will result in a tetanic contraction. The choice of treatment parameters will depend
on the desired effect, but to combine muscle stimulation with an increase in blood flow and a possible reduction in edema, there is some logic in selecting a range which does not involve strong sustained tetanic contraction & a sweep of 10-25Hz .
3. Edema
IFT has been claimed to be effective as a treatment to promote the reabsorption of edema in the tissues.
4. Blood flow
There is very little, if any quality evidence demonstrating a direct effect if IFT on local blood flow changes. Most of the work that has been done involves laboratory experimentation on asymptomatic subjects, and most blood flow measurements are superficial i.e. skin blood flow. Whether IFT is actually capable of generating a change (increase) in blood flow at depth remains questionable. The elegant experimentation by Noble et al (2000) demonstrated vascular changes at 10–20Hz, though was unable to clearly identify the mechanism for this change. The stimulation was applied via suction electrodes, and the outcome could therefore be as a result of the suction rather than the stimulation, though this is largely negated by virtue of the fact that other stimulation frequencies were also delivered with the suction electrodes without the blood flow changes. The most likely mechanism is via muscle stimulation effects (IFT causing muscle contraction which brings about a local metabolic and thus vascular change). The possibility that the IFT is acting as an inhibitor or sympathetic activity remains a theoretical possibility rather than an established mechanism.
Based on current available evidence, the most likely option for IFT use as a means to increase local blood flow remains via the muscle stimulation mode, and thus the 10-20 or 10-25Hz frequency sweep options appears to be the most likely beneficial option.
- Patients who do not comprehend the physiotherapist’s instructions or are unable to co-operate should not be treated
- Patients with Pacemakers – some pacemakers are relatively immune to interference from electrical stimulation whilst others can demonstrate serious adverse behaviour. It is suggested that as a general rule, if the patient has a pacemaker, it is best to avoid all electrical stimulation, but like TENS, if it is a treatment that is needed. The stimulation should be tried in a carefully controlled environment where appropriate equipment is available to correct any pacing problems should they arise.
- Patients who are taking anticoagulation therapy or have a history of pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis should not be treated with the vacuum electrode applications
- Similarly, patients whose skin may be easily damaged or bruised.


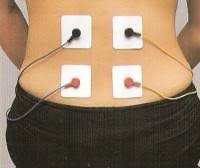


Application over :
The trunk or pelvis during pregnancy (though this MAY be modified in time in line with the TENS advice. At the present time, it is suggested that it is best avoided in these regions) ? Active or suspected malignancy except in hospice/palliative/terminal care
- The eyes
- The anterior aspect of the neck
- The carotid sinuses
- Dermatological conditions e.g. dermatitis, broken skin
- Danger of hemorrhage or current tissue bleeding (e.g. recent soft tissue injury)
- Avoid active epiphyseal regions in children
- Transthoracic electrode application is considered to be ‘risky’ by many authorities
Interferential Precautions
- Care should be taken to maintain the suction at a level below that which causes damage / discomfort to the patient
- If there is abnormal skin sensation, electrodes should be positioned in a site other than this area to ensure effective stimulation
- Patients who have (marked) abnormal circulation
- For patients who have febrile conditions, the outcome of the first treatment should be monitored
- Patients who have epilepsy, advanced cardiovascular conditions or cardiac arrhythmias should be treated at the discretion of the physiotherapist in consultation with the appropriate medical practitioner
- Treatment which involves placement of electrodes over the anterior chest wall.